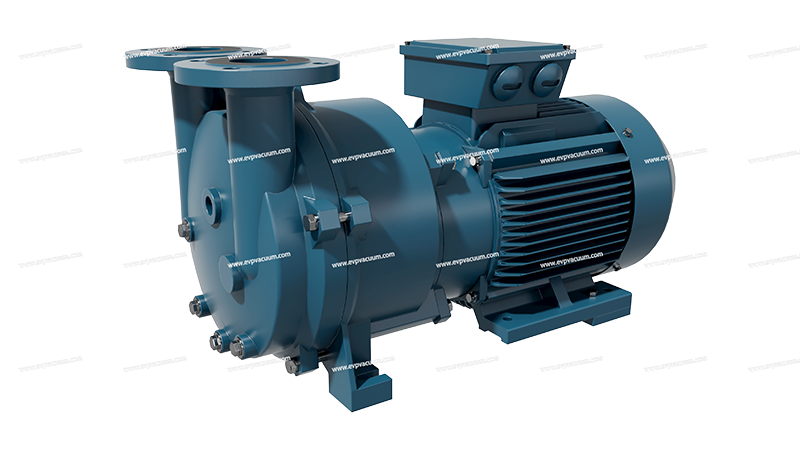
Autoclave Sterilizer for Liquid Ring Vacuum Pumps
EVP liquid ring vacuum pump 2BV series is used in autoclaves
Vacuum pumps play a vital role in autoclaves (especially modern, high-performance sterilizers). Their main function is to remove air from the sterilization chamber and the packaging of sterilized items.
EVP’s 2BV and DLV series liquid ring vacuum pumps can meet customer needs very well.
For example, the following three representative autoclave customers:
Inquiry products: 2BV2-061, 2BV2-070, DLV-110
Required material: cast iron material, impeller SS304. The contact medium is only water, and the cast iron + SS304 impeller is sufficient to cope with the working conditions.
Size requirements: as small as possible
The following are specific applications of vacuum pumps in autoclaves:
1. Pre-vacuum stage (the most critical application):
(1) Purpose: Before steam is introduced for sterilization, remove the air inside the sterilization chamber and sterilized items (especially porous items, tubular instruments, and packaged items) as thoroughly as possible.
(2) Reasons: Air is the enemy of steam sterilization:
① Hinder heat transfer: Air forms an insulating layer (air mass) that prevents high-temperature steam from effectively and quickly contacting and penetrating all surfaces, gaps, and interiors of items.
② Reduce actual temperature: The temperature of the air-steam mixture is lower than the temperature of pure saturated steam at the same pressure. For example, at a saturated steam pressure of 121°C, if air is present, the temperature of the mixture may be only 100°C or lower, and the effective sterilization temperature cannot be reached.
③ Cause sterilization failure: The presence of air masses will cause “cold spots”, making it impossible for the area to reach the necessary sterilization temperature and exposure time, resulting in sterilization failure.
(3) Vacuum pump function: By vacuuming, the air content in the chamber is greatly reduced, creating conditions for uniform penetration and efficient heat transfer of subsequent pure saturated steam.
2. Pulsating vacuum process (enhanced effect):
(1) Purpose: To further improve the efficiency of air removal, especially for items that are difficult to penetrate (such as wrapped fabrics, instruments with long lumens, and porous loads).
(2) Process: After the vacuum pump pumps the chamber to a set negative pressure (vacuum), it injects a small amount of steam into the chamber (to increase the pressure) and then vacuums it again with the vacuum pump. This “vacuuming-injecting steam-vacuuming again” process will be repeated many times (such as 3 times).
(3) Principle: Each injection of steam helps heat the item, displace residual air and make it easier to be extracted (steam diffuses into the air mass, diluting and carrying air). Multiple pulsations significantly improve the thoroughness of air removal and are the gold standard for handling complex loads.
3. Drying phase:
(1) Purpose: After the sterilization cycle is completed, remove the condensed water remaining in the sterilized items (especially fabrics and packaging materials) and the chamber.
(2) Reason: Wet packages or instruments are prone to bacterial growth during storage (humidity is a medium for microbial growth) and are also prone to packaging damage.
(3) Vacuum pump function: After the sterilization is completed and the steam is exhausted, the vacuum pump starts to evacuate the air again. Under vacuum, the boiling point of water is significantly reduced (below 100°C), so that the residual water evaporates (boils) rapidly at a relatively low temperature and is pumped out of the chamber by the vacuum pump, achieving fast and effective drying.
Summary
The EVP 2BV series vacuum pump has become a core component of modern autoclaves through efficient degassing, deep drying and safety design. Its technical advantages (such as isothermal compression, corrosion-resistant materials) and flexible configuration (explosion-proof motor, ejector extension) can meet the full range of scenarios from ordinary laboratories to high-safety medical sterilization. When selecting a sterilizer, it is necessary to consider the characteristics of the sterilized items (such as porosity, chemical residue risk) and equipment compatibility to maximize sterilization efficiency and safety.
(The article comes from the Internet. If reprinting is not allowed, please contact our company to delete it.)