Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump replaces Finder CDS pump for fertilizer plant
Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump used in Urea and melamine formaldehyde resins production plant
The most outstanding feature of wood adhesives is their large dosage. The cost, variety and quality of adhesives directly affect the cost, quality and use of artificial boards. Therefore, most wood processing companies in various countries have their own glue-making workshops. The main types of glue they produce are urea-formaldehyde resin glue, phenolic resin glue and Melamine resin glue. At the same time, with the increase in the variety of wood glue products and the continuous improvement of their quality requirements, specialized glue-making enterprises have emerged.
The main equipment of the glue making workshop is the reaction kettle, condenser and vacuum pump, high-level storage tanks and weight measurement tanks (or tanks) for various raw materials. Some auxiliary equipment is also needed, such as infusion pumps, water storage tanks, vacuum tanks, and dehydration tanks. , glue storage tank, gas-water separator, etc.
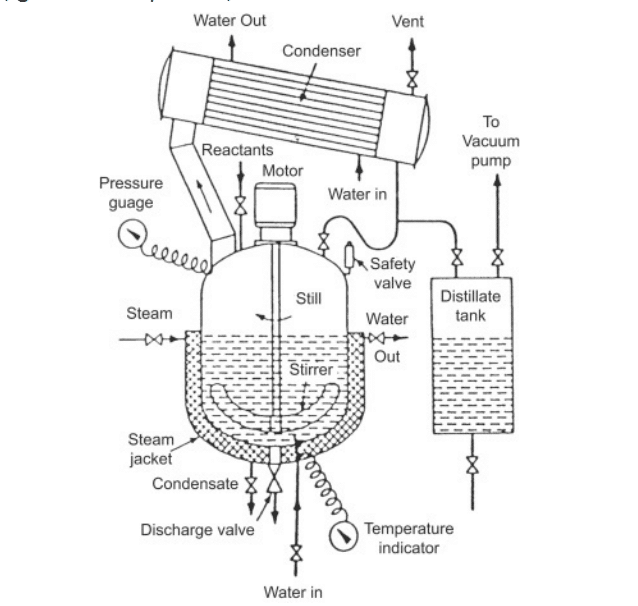
The reaction kettle is one of the main equipment for preparing synthetic resin. It consists of three parts: the kettle body, the stirrer and the reducer.
Reaction kettle body The kettle body is the place where materials are stirred and undergo chemical reactions. The actual volume of the reaction kettle is the volume of the kettle body. However, during production, the material may foam or boil, causing the volume of the material to increase, so the charging volume is generally smaller than the actual volume of the reactor. There is the following relationship between them:
V outfit = V0·ɧ
In the formula: V1 is the charging volume
V0 is the actual volume
η is the charging coefficient (or loading coefficient)
The charging coefficient n is determined based on actual production conditions or test results.
If dehydrated resin is produced, eta is 0.750.8, and when non-dehydrated resin is produced, eta can reach 0.9.
“Vacuum” refers to a state in which the density of gas molecules in a given space is lower than the atmospheric pressure of the area. There are many types of vacuum pumps. According to their different structures, they can be divided into reciprocating type, rotary type (rotary vane type and Rotary Piston type), water ring type and jet type. These types of vacuum pumps have been used in glue making workshops. At present, most glue-making workshops in the wood industry use water ring vacuum pumps, and a few factories use rotary vane vacuum pumps. There are also individual factories that are trying out jet vacuum pumps.
In addition to the above three main equipment, the glue making workshop also needs some auxiliary equipment to ensure the implementation of the glue making process. These auxiliary equipment are mainly liquid and solid material transportation equipment: infusion pumps/centrifugal pumps, raw material metering equipment, raw material and product storage tanks, and other vapor-liquid separator etc.
Solid materials (such as urea and melamine) in solid material conveying equipment are generally packed in bags and need to be transported to the feeding table using an electric hoist. When solid materials are added to the reactor, most of them are now poured into the feeding hole of the feeding table, allowing the material to enter the funnel at the feeding port from the feeding pipe, and then into the reactor. There are also mechanical urea feeding devices (such as screw propellers or belt conveyors). device) for feeding.
Container equipment: including formaldehyde storage tanks (single volumes are 50m3, 100m3, 200m3), glue storage tanks, condensate storage tanks (for dehydration), buffer tanks, metering tanks, etc. These are non-standard equipment and can be customized according to the specific requirements of the factory. Design and manufacture according to conditions and production requirements. The volume and quantity of formaldehyde solution storage tanks are determined by production volume. Generally, the storage capacity should be enough for at least two days of production. There needs to be a heating device inside or outside the storage tank to ensure that the temperature of the formaldehyde solution can be around 15°C during the low temperature season in winter. After the storage tank is filled with formaldehyde solution, samples should be taken to measure the formaldehyde and methanol content before use. Set. Both the phenol metering tank and the melamine storage tank should have thermal insulation equipment.
Measuring equipment: Flow meters and liquid level meters can be used to measure liquid materials. It is best to use weight measurement and scales, while scales are often used to measure solid materials. Pressure-sensitive electronic metering devices can be used in reactors and urea metering devices of large-scale production equipment.
Glue making workshop process flow
There are currently three types of technological processes in the glue making workshop: batch method, pre-condensation batch method and continuous method. The intermittent method is commonly used in our country, while all three processes are available abroad.
Take the batch process as an example: the process is a single reactor. Add the required raw materials into the reactor in proportion, and then react according to the reaction process conditions until the initial resin is formed, then cool and discharge. The advantage of this process is that the operating conditions can be changed at any time as needed, and it is highly flexible and suitable for multi-variety production. However, it has the disadvantages of low production efficiency and the need for a lot of equipment. The process is as above:
After melting, the phenol can be pumped into the reactor by vacuum suction method, or it can be pumped into the metering tank first (a heat preservation device is required) and then added to the reactor. Other liquid raw materials are generally pumped into the metering tank using a vacuum suction method, and then placed into the reaction kettle using a high position. Solid raw materials (such as urea and melamine) are usually placed on a three-layer platform obliquely above the reactor. There are feeding holes on the platform. After the urea is weighed (or measured in bags), it is added to the feeding holes manually or mechanically. Connect an inclined slide to the addition funnel on the reactor. The reaction kettle is connected to the vacuum system through the condenser, and the metering tank is directly connected to the vacuum system. At present, formaldehyde is generally pumped into the metering tank, while phenol is sucked into the metering tank using a vacuum pump.
The cooling water circulation enters from the lower end of the reactor or condenser and outputs from the upper end. If the cooling water is reused, it can be cooled by the cooling tower and flow to the storage pool, and then pumped to the water tank for later use. If there is a reflux process in the production of phenolic resin, a reflux pipe needs to be connected under the condenser and returned to the reactor. The reflux pipe generally has a U-shaped elbow to create a liquid seal so that the reflux can proceed smoothly. There are condensate storage tanks or dehydration tanks and buffer tanks between the vacuum pump and the condenser. Some also install several gas-water separators between the buffer tank and the vacuum tube. These auxiliary equipment can minimize the gas entering the vacuum pump. or contain no moisture or corrosive substances.
Water ring vacuum pumps are mainly used for rough vacuuming in processes with large air extraction volumes. Its advantages are simple and compact structure, maintenance-free, reliable operation, easy to use, strong durability; It can pump corrosive gases, dust-containing gases and gas-water mixtures, no piston, rarely blocked, safe and reliable, and low noise. The appropriate temperature of the pumped gas is -20~40℃. The ultimate vacuum of the single-stage water ring vacuum pump can reach 92%~98% (8.1~2kPa), and the ultimate vacuum of the two-stage water ring vacuum pump can reach 99.9% (0.11kPa). The pumping capacity is 110~1600m3/h.

Take EVP customers as an example:
Their operating medium parameters are air 90%, formalin 2,5%, water 4%, methanol 2,5%, urea (dust) 1%,
Standard:
Temperature is 32 °С
System volume is 40 m³
Tank leakage rate, 2.5mbar/min
Suction pressure is 53mbar
Min.:
Temperature is 25 °С
System volume is 8 m³
Tank leakage rate, 1.7mbar/min
Suction pressure is 40mbar
Max.:
Temperature is100 °С
System volume is 145m³
Tank leakage rate, 3.8mbar/min
Suction pressure is 1013mbar
Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump requirement parameters
Flow rate is 637m³/h
Release volume is 40m3
Release time is 7min
Initial suction pressure is 1013mbar
Final suction pressure is 53mbar
Discharge pressure is 1013mbar
Water temperature in the liquid ring is 10°С
Operating mode is intermittent
The vacuum pump is used at different stages of the batch, but usually not when the separator tank is empty. As a rule, the tank is filled to 75% before a small vacuum of up to 100mbar abs is required. The most demanding part of the vacuum pump operation is when the batch is completed (the tank is 90% full) and the highest vacuum value is required for rapid evaporation of water from the batch.
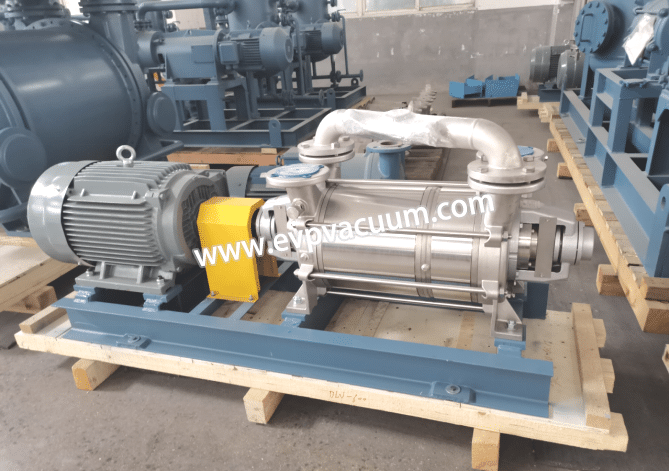
The limitation is the cooling capacity of the condenser in summer, which cannot reach temperatures below 32 °C. The existing pump model used in the production Finder CDS NP 730 with separator, which replaced by EVP DLV-1200two-stage liquid ring vacuum pump with SS304 separator
Client Purchased 2Set EVP brand DLV-1200 Two-stage liquid Ring Vacuum Pump with Separator systems
Application: replace Finder CDS NP 730, used in Urea and melamine formaldehyde resins production plant
EVP DLV-1200 Two-stage liquid Ring Vacuum Pump information:
Complete SS304 with Mechanical seal
Motor: 6P-37KW IP56 IE3 Ex DIIB T4 GB Voltage : 380V @ 50Hz
Max.Pumping Speed :1252m3/h
Ultimate Vacuum: 33mbar
The synthesized resin is released from the discharge port at the bottom of the reactor. It can be placed in a small bucket or in a glue storage tank. When needed, it can be transported to the glue-using workshop with a pump. In addition to cooling the reactor itself, the synthetic resin adhesive can also be cooled by a heat exchanger.
The intermittent process flow is more flexible. Wood processing companies all have their own glue-making workshops. The resin produced is mainly suitable for wood factories, and the output is not very high. However, some large factories have many product varieties, so they produce many types of resin and the output is high. They are not the same, so operating with a single kettle can give full play to its flexibility and meet the needs of the wood industry.
Regardless of whether the glue making workshop produces phenolic resin, urea-formaldehyde resin or melamine resin, a certain amount of wastewater will be discharged. For example, the water extracted from decompression and concentration, washing kettle water, tank washing water, and floor flushing water may contain a small amount of harmful substances. These harmful substances mainly include phenol, formaldehyde, methanol, etc. Therefore, synthetic resin production wastewater needs to be properly treated to meet national standardization requirements and reduce wastewater pollution of water resources.
For more details, please consult Shanghai EVP Vacuum Technology Co., Ltd.
(The article comes from the Internet. If reprinting is not allowed, please contact our company to delete it.)
