molecular pumps in PVD of application
PVD process of application
Molecular pumps play a critical role in physical vapor deposition (PVD) processes, primarily by achieving and maintaining a *high vacuum or ultra-high vacuum environment* (typically ranging from 10-3 to (10-8Torr) within the vacuum chamber. Below is a detailed explanation of their specific functions, working principles, and applications:
1. Role of Molecular Pumps in PVD
(1) Rapid High Vacuum Establishment
– PVD processes (e.g., sputtering, evaporation, ion plating) require an environment with minimal gas molecules to reduce contamination of deposited thin films (e.g., oxidation, impurity incorporation). Molecular pumps rapidly evacuate the chamber pressure from low vacuum (achieved by mechanical pumps, down to 10-3 Torr to high vacuum (below (10-6 Torr).
(2) Maintenance of a Clean Vacuum Environment
– Molecular pumps are **oil-free vacuum pumps**, avoiding contamination from oil vapor backflow (a potential issue with traditional oil diffusion pumps). This ensures film purity and process stability, which is crucial for sensitive applications like semiconductor fabrication and optical coatings.
(3) Precise Control of Gas Atmosphere
– In reactive PVD (e.g., reactive sputtering of titanium nitride), precise introduction of reaction gases (e.g., nitrogen) is required. The high pumping speed of molecular pumps dynamically balances gas flow rates, maintaining stable vacuum levels and ensuring controlled chemical reactions.
2. Working Principle of Molecular Pumps
Molecular pumps transfer momentum to gas molecules via high-speed rotating rotor blades (reaching tens of thousands of RPM), directing the molecules toward the pump outlet, where they are expelled by a backing pump (e.g., a mechanical pump). Key features include:
– **Molecular Flow Regime**: Efficient operation at low pressures (molecular flow regime), unlike viscous flow at higher pressures.
– **High Compression Ratio**: Maintains high compression even for light gases (e.g., hydrogen), making it ideal for evacuating residual gases in PVD.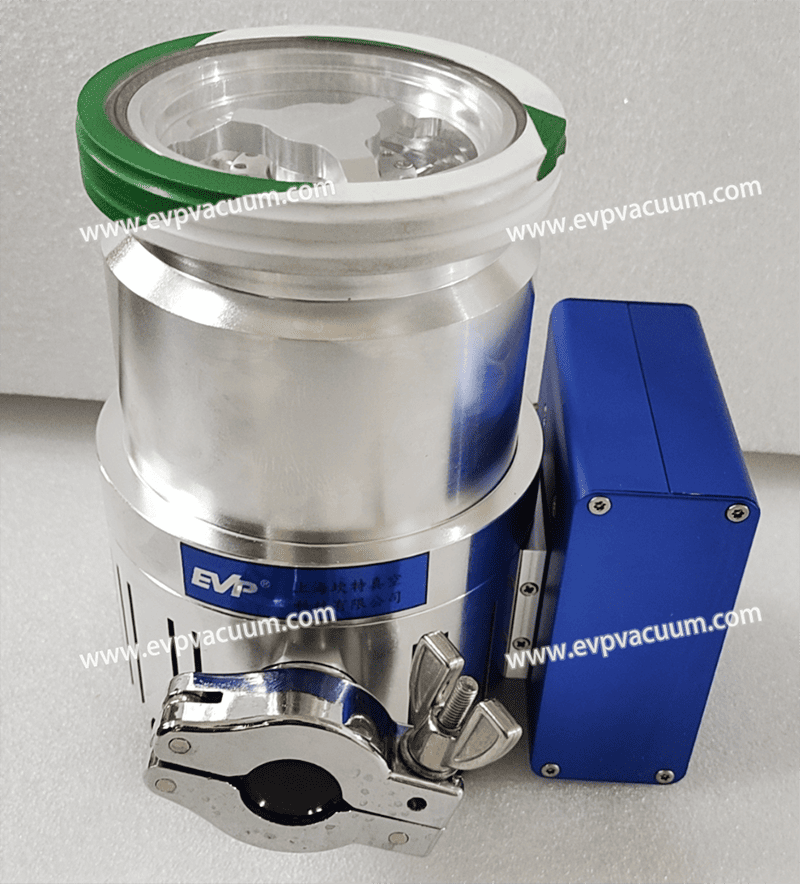
3. Typical Molecular Pump Configurations in PVD
(1) Multi-Stage Pumping System
– **Backing Pump**: A mechanical or dry pump reduces pressure from atmospheric to 10-3 Torr.
– **Molecular Pump**: Serves as the main pump, further lowering pressure below 10-6 Torr.
– **Optional Auxiliary Pump**: For ultra-high vacuum requirements, ion pumps or cryopumps may be added.
(2) Application Examples
– **Magnetron Sputtering**: Molecular pumps maintain high vacuum for sputtering while evacuating process gases (e.g., argon).
– **Electron Beam Evaporation**: Molecular pumps sustain vacuum levels of 10-7 Torr to prevent residual gas interference with electron gun operation.
4. Key Parameters for Molecular Pump Selection
– **Pumping Speed (L/s)**: Determined by chamber volume and required evacuation time.
– **Ultimate Vacuum**: Turbo molecular pumps typically reach 10-10 Torr; compound pumps cover medium-to-high vacuum ranges.
– **Particulate Resistance**: Models with protective designs are preferred to handle micro-particles generated during PVD.
5. Maintenance and Considerations
– **Particulate Contamination Prevention**: Install filter screens at the pump inlet to block coating particles from damaging blades.
– **Regular Maintenance**: Inspect bearing lubrication and replace worn rotor components.
– **Safe Shutdown**: Avoid sudden power loss to prevent rotor stall; use backup power or controlled deceleration systems.
Molecular pumps are core components of PVD systems, enabling high-performance thin-film deposition through their oil-free operation, high pumping speed, and precise vacuum control. These attributes directly influence film density, adhesion, and purity. As PVD technology expands in semiconductor, new energy, and other fields, the reliability and adaptability of molecular pumps will remain critical for process optimization.
(The article comes from the Internet. If reprinting is not allowed, please contact our company to delete it.)



