Vacuum pump of principle diagram
Diffusion pump (oil diffusion pump)
In 1915, German physicist W. Gade published his report on diffusion pump. In 1916, American I. Langmuir made a so-called condensate pump with a cooling system on the pump wall. Using mercury vapor as working medium, these pumps can obtain a vacuum of 10-5 PA. In 1928, Englishman C.D. Burch found high boiling point petroleum derivatives. In 1936, C.D. Hickman and others made synthetic oil. The saturated vapor pressure of these two kinds of oil is very low at room temperature, so they replace mercury as the working fluid of diffusion pump. Since then, oil diffusion pump has been widely used in industrial production and scientific experiments in the field of high vacuum, and laid the foundation of high vacuum technology. Since the 1960s, the oil diffusion pump has a new development.
The main improvements are:
① The material of the pump is stainless steel with very small air release.
② The oil with low saturated vapor pressure and good thermal stability, such as polyphenylene ether and silicone oil, is used as the working fluid of the pump.
③ The structure of the new type of oil diffusion pump is reformed. Under the condition that the pump port flange is constant and the pump boundary dimension is not changed, the section of the pump cavity is enlarged prominently at the lower part of the flange, and the pumping rate can be increased by 20-40%. For example, a large diameter diffusion nozzle and a large diameter oil baffle cap cooled by liquid nitrogen are installed here. The pump can have the pumping rate of the normal pump (the pump without enlarging the section of the pump chamber), and completely overcome the return oil of the pump and obtain a clean ultra-high altitude of less than 10-8 PA. Therefore, the oil diffusion pump plays an important role in the industrial production and scientific test of clean ultra-high vacuum.
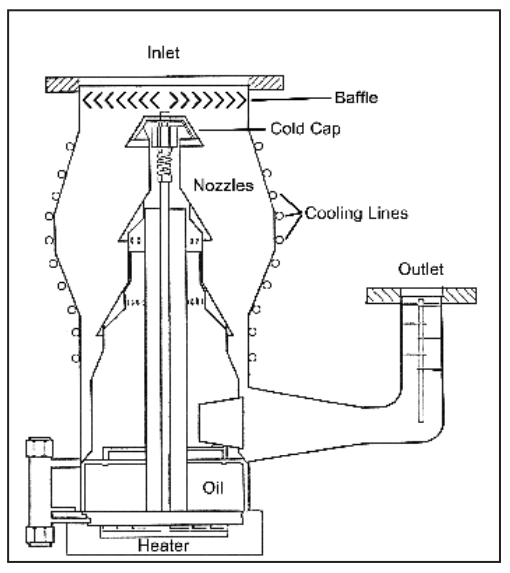
Diffusion pump structure and working principle
The oil diffusion pump is mainly composed of pump body, diffusion nozzle, steam conduit, oil pan, heater, diffuser, cooling system and spray nozzle (see Figure). When the vacuum of the oil diffusion pump is less than 1 pa, the oil pan can be heated. When boiling, the nozzle ejects high-speed steam flow. The hot gas molecules diffuse into the steam flow and collide with the directional oil vapor molecules. Therefore, the momentum of gas molecules is obtained and the directional flow in the same direction as that of oil vapor molecules is generated. To the former stage, the oil vapor is condensed and the gas molecules are released, that is to say, it is pumped away by the former stage pump to achieve the purpose of pumping.
The vapor pressure of the pump oil directly affects the vacuum performance of the pump. But any pump oil used in the oil diffusion pump is a multi-component mixture with different vapor pressure. Therefore, in order to improve the pumping and vacuum performance of the oil diffusion pump, the pump itself needs to fractionate and purify the pump oil. The purpose of fractionation is to keep the oil with high vapor pressure component from entering the high vacuum working nozzle (nozzle at high vacuum end); the purpose of purification is to make the oil with high vapor pressure component continuously removed by the front pump during the working process, so that the oil will gradually become pure
Pump oil fractionation mainly uses the different evaporation temperature of each component of pump oil to make them evaporate on different boiler areas. When the pump oil condensed and returned after operation flows to the pump wall with a heat preservation cover, the oil is preheated and then flows to the periphery of the oil pan. After being heated by the annular heater at the bottom of the pan, the light fraction oil reaches the evaporation temperature and evaporates in the outer layer and enters the low vacuum working nozzle (close to the nozzle of the previous stage pump); some light fraction oil that fails to evaporate also floats to the oil surface due to its smaller specific gravity than other fraction oil.
Due to the limitation of the outer steam pipe, this fraction still enters the low vacuum working nozzle after evaporation. The heavy fraction oil did not evaporate because it did not reach the evaporation temperature in the outer steam pipe, so it flowed from the gap between the bottom of the pot to the center of the oil pot for evaporation and entered the high vacuum working nozzle. The oil vapor of light and heavy fractions is divided into low vacuum working nozzle and high vacuum working nozzle, which is called fractionation. The oil vapor ejected from the jet nozzle is not sufficiently cooled in the front stage, and the light fraction in the vapor is not completely condensed and is pumped out by the front stage pump.
With such circulation, the light fraction in the pump oil is less and less, the proportion of heavy fraction is larger and larger, and the pump oil tends to be pure gradually. This process is called purification. The fractionation and purification of pump oil plays an important role in improving the limiting vacuum of pump.
When the diffusion pump is working, the appropriate cooling water must be introduced first, and then the oil pan shall be heated; at the end of the work, the power supply of the heater shall be cut off first, and then the cooling water shall be closed when the pump is cooled to near the room temperature. When using the pump, do not cut off the water. If the water is cut off suddenly, turn off the electric furnace. The inlet and outlet of the cooling water must be tied tightly to prevent the pipe from falling off when the water pressure is high. After the discharge is ready, turn on the mechanical pump and other systems when the vacuum degree reaches 10-2Pa before turning on the electric furnace for heating. Turn on the cooling water at the same time.
Cut off the heat source after use, and stop the mechanical pump after the pump cools down. To prevent oxidation of “working fluid”.


