What is short-path distillation?
Many materials such as heavy petroleum residues, chemicals, medicines, natural foods, health products, fatty acids, etc. are often heat-sensitive, viscous and/or have high boiling points. To separate these materials from their other components and maintain the quality of the product, they can only be distilled at a low boiling temperature or even below the boiling temperature, and only in a very short time to minimize thermal decomposition or polymerization to eliminate damage to the product.
Short-path distillation characteristics:
Short residence time: The scraper makes the liquid film stay on the heating surface for a very short time.
Low distillation: temperature Since the condenser is directly opposite the heating surface, the pressure difference is reduced, so it has a very high vacuum degree. The material can be distilled at a very low temperature or even without reaching the boiling point.
Viscous materials and products containing solids: The deep immersion of the scraper, relying on a considerable edge, the material film causes a strong shear and mixing effect, reducing the viscosity of the liquid to be treated, suitable for processing viscosity up to 50Pas, and prevents scaling of the heating surface, especially suitable for solid-containing liquid.
Extremely thin distillation liquid surface: The scraper scrapes the liquid into an extremely thin liquid film. More thorough separation.
High separation ratio: The precision scraper uses an extremely thin liquid film that is evenly distributed on the heating surface, resulting in the entire heating surface being wetted. This allows the operating unit to have a high boiling separation ratio. This means that more than 90% of the incoming in the case is evaporated, and a constant level of residual substances can be achieved.
Working principle
The pressure difference between the boiling film and the condensing surface is the driving force for the flow of steam. A small pressure drop will cause the flow of steam. Operation at 1mbar requires a very short distance between the boiling surface and the condensing surface. The distiller made based on this principle is called a short-path distiller. The short-path distiller (molecular distillation) has a built-in condenser opposite the heating surface and reduces the operating pressure to 0.001mbar.
The short-path distiller is a thermal separation technology process that works at a pressure of 1~0.001mbar. Its low boiling temperature is very suitable for heat-sensitive and high-boiling-point substances. Its basic structure is a cylindrical barrel with a heating jacket, a rotor and a built-in condenser. The rotor is precisely equipped with a scraper and a splash guard on the rotor’s fixed frame. The built-in condenser is located in the center of the evaporator, and the rotor rotates between the cylindrical barrel and the condenser.
The short-path distiller consists of an externally heated vertical cylindrical body, a central condenser located therein, and a film scraper rotating between the distiller and the condenser.
The distillation process is as follows: the material is added from the top of the evaporator, and is continuously and evenly distributed on the heating surface by the liquid distributor on the rotor, and then the film scraper scrapes the liquid into a very thin, turbulent liquid film, and propels it downward in a spiral. In this process, the light molecules escaping from the heating surface condense into liquid on the built-in condenser through a short route and almost without collision, and flow down along the condenser tube, and the residual liquid, that is, the heavy molecules, are discharged through the discharge pipe located at the bottom of the evaporator and collected in the circular channel under the heating zone, and then flow out through the discharge pipe on the side.
Typical Applications
| Application industries | Names of refined items: |
| Food industry | Monoglyceride, palm oil, tocopherol, cod liver oil, squalene, rice bran oil, fatty acids and their derivatives, dienoic acid vegetable oil, diglyceride, lactic acid, linseed oil, conjugated linoleic acid |
| Pharmaceutical industry | Acid chloride, amino acid ester, vitamin E, glucose derivatives, terpene esters, natural or synthetic vitamins, B-carotene, gingerol, capsicum pigment |
| Chemical industry | Erucamide, alcohol, oleamide, glyceride, herbicide, halogenated alkanes, pesticide, silicone oil, wax, dibasic fatty acid, dimer acid |
| Plastic industry | Epoxy resin, epoxidized oil, isocyanate, plasticizer, stabilizer |
| Petroleum industry | Base oil, bright oil, lubricating oil, vaseline, fir oil, residual tar, waste lubricating oil |
| Cosmetic industry | Lanolin, lanolin, lanolin alcohol, alkyl polyglycosides, rose oil, ginger oil, capsanthin, etc., including extracts of algae roots and pepper plants |
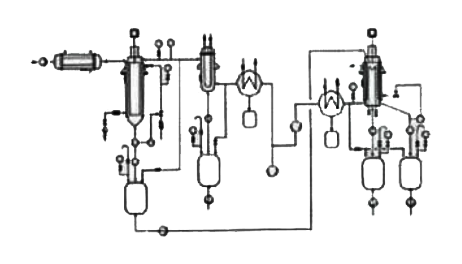
a) Short-path distiller single-stage distillation unit:
The preheated and degassed material enters the short-path distiller, where the light component is evaporated and condensed on the built-in condenser, and it and the heavy component are discharged from different channels.
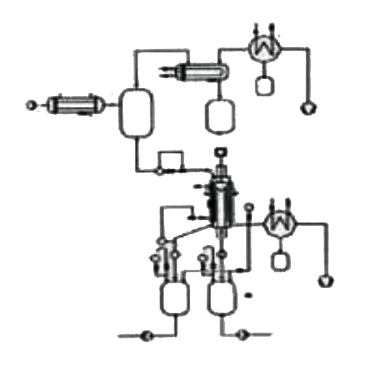
b) Combined distillation unit of wiped film evaporator and short path distiller:
A large amount of low boiling substances are removed in the wiped film evaporator, and the product is distilled in the subsequent short path distiller.