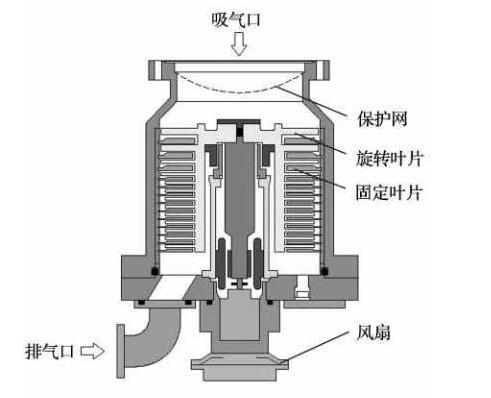
Molecular pump structure and schematic diagram
The core components of molecular pumps are rotating blades and fixed blades. The speed of rotating blade reaches 1800 ~ 90000rpm, and the speed of blade end reaches hundreds of m/s, which is close to the average speed of molecules. The gas molecules are transported to the exhaust port through the collision with gas molecules. When rotating the rotating blade toward the set at high speed, the probability of the gas molecules moving from the suction side to the exhaust side is A, and the probability of the gas molecules moving from the exhaust side to the suction side is B. When the rotating blade hits the gas molecules, the gas molecules touch the fixed blade and then fly to the next rotating blade again, which is eventually bounced to the exhaust port, making A>B realize the exhaust function.
If the blade Angle is large, the exhaust speed is large and the compression ratio is small. When the blade Angle is small, the exhaust velocity is small and the compression ratio is large. The exhaust speed of the molecular pump is basically unaffected by the type of gas. The ultimate pressure of the pump can reach 10-8 Pa, but for light molecules/atoms, the exhaust speed will be reduced.
Molecular pump is a kind of high speed rotating mechanical pump, so the requirement for balance is very high, and it is very fragile to solid foreign matter. Metal filter screen is usually installed at the entrance of molecular pump. During the operation of the molecular pump, if the pressure deteriorates suddenly, the blade may be damaged.
Conventional molecular pumps use bearings to ensure high-speed rotation of blades. The new type of molecular pump adopts magnetic levitation structure, which makes the blade speed increase continuously while making the molecular pump more suitable for ultra-high vacuum system and prolongs the service life of molecular pump.
Compared with oil-sealed rotary vane pump and turbine dry pump, the working environment of molecular pump is cleaner and the vacuum degree can be very high. However, molecular pumps cannot operate at atmospheric pressure and must be used in combination with other crude vacuum pumps (oil-sealed rotary vane pumps or turbo-dry pumps) that can operate at atmospheric pressure. Molecular pumps are complex, expensive and vibrate at high speed.
(The article comes from the Internet. If reprinting is not allowed, please contact our company to delete it.)
