Vacuum Pump for Sugar Vapour Condenser
Liquid ring vacuum pumps are usually used to treat wet gas mixtures (i.e. mixtures containing condensable vapors). The moisture in the mixture can wash the lubricant in the traditional “dry” oil lubrication pump, which may lead to premature failure.
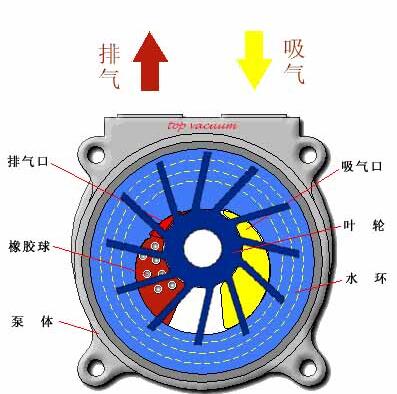
Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump Working Principle
When the impeller of the vacuum pump rotates, it throws water through centrifugal force to form a concentric liquid ring around the shell, thus carrying out compression operation. The eccentric installation of the impeller relative to the shell results in an increase in the spacing between the impeller blades at the entrance and a decrease in the spacing towards the exit. When the gas enters the inlet, it is trapped between the impeller blade and the liquid ring. Then, as the impeller rotates, the liquid ring compresses the gas and forces it out of the outlet.
How to Determine the Dimension of Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump
The information needed to accurately determine the size of the liquid ring vacuum pump includes:
1. Inlet pressure, usually expressed in mm Hg
2. Inlet temperature
3. Mass flow rate, usually expressed in kg/hr, molecular weight of fluid components
4. Steam pressure data for each fluid component
5. Sealing fluid data, if not water: specific gravity, specific heat, viscosity, thermal conductivity, sub-6. Molecular weight and vapor pressure data
7. Temperature of Sealing Fluid or Cooling Water
8. Exhaust pressure, usually expressed as kPa G
Each of these factors affects the size of the liquid ring vacuum pump.
Many manufacturers of liquid ring vacuum pumps have issued 60 F dry air curves for sealed water. According to these curves, correction is made to take into account the actual operating conditions.
When using sealed fluids other than water, manufacturers of liquid ring vacuum pumps will need specific gravity, specific heat, viscosity, molecular weight and steam pressure data to accurately correct the dry air curve.
By decrypting the vapor pressure of the sealing fluid, the manufacturer can check the cavitation and determine its effect on capacity. If the vapor pressure of the sealing fluid is less than the vapor pressure of the water, the dry air capacity of the pump increases. This is because less sealing fluid will blink and occupy the space between the impeller blades. If the vapor pressure of the sealing fluid is greater than that of the water, the reverse is true.
The operating horsepower can be calculated by knowing the specific gravity and viscosity of the sealing fluid. The pump curve is usually based on water as a sealing fluid, and then determines whether the operation or braking horsepower increases or decreases. The higher the specific gravity and viscosity, the greater the braking power required by the pump. If the sealing fluid is oil, the braking horsepower is usually less than the braking horsepower of water, and if it is ethylene glycol, the opposite is true.
Load type of liquid ring pump will affect its capacity. The two basic types are dry air load and saturated air mixture.
For dry air loads, air enters the impeller barrel through the inlet, where it contacts the sealing fluid. Dry air saturates immediately through the water in the evaporating liquid ring.
Evaporated water from the liquid ring occupies the space in the impeller barrel. This reduces the new air intake that the impeller bucket can handle, which may lead to the selection of larger vacuum pumps.
For saturated air mixtures, the load enters the impeller barrel through the inlet, but condensation occurs if the sealing fluid is cooler than the incoming gas mixtures. This allows more space in the impeller barrel to handle additional air intake and use smaller vacuum pumps.
The only way the manufacturer can correctly determine the size of the liquid ring vacuum pump is to understand the composition and properties of the gases that make up the mixture. This will allow the manufacturer to make appropriate corrections and select the best pump.
The discharge pressure of the pump is required to determine any reduction in pump capacity or any increase in operating horsepower.
Most liquid ring vacuum pumps are designed for pumping from vacuum to atmospheric emission pressure. If the discharge pressure increases, more energy or braking horsepower is required to operate within the increased compression range. By changing the discharge pressure, the efficiency of the pump can be changed and the capacity of the pump can be reduced to compensate for this larger compression range.
Manufacturers of liquid ring vacuum pumps can determine whether cavitation can be generated by specific applications. Cavitation occurs due to the rapid boiling of sealed liquids. During boiling, bubbles form in liquids and seek escape. As bubbles rise in liquids, they withstand higher pressure zones and may collapse. The void space left by the collapse of bubbles is filled with liquid immediately. This phenomenon leads to a large number of erosion or pitting corrosion inside the pump.
Cavitation can be detected by rumbling, which sounds like marble rolling inside the pump. This sound should not be confused with the sound caused by the “water hammer”. If the vapor pressure of the sealed fluid is close to the working inlet pressure of the vacuum pump, the sound heard is probably due to cavitation.
If the liquid ring pump is disassembled and the impeller and the port plate are indented, the cavitation will obviously occur. The liquid ring pump with flat end plate can be easily machined and reassembled. On the contrary, because of the taper and angle of the cone, the liquid ring pump with tapered port is more difficult to process.
The possible ways to eliminate cavitation erosion are:
Use cooler sealing fluid. This will reduce the vapor pressure of the sealing fluid and prevent it from flashing.
Use sealing fluid with lower vapor pressure. This prevents the sealing fluid from flickering and causes cavitation. Sealing fluid should be compatible with process gas mixture and structural material. Some accessories may need to be redesigned to operate with this different sealing fluid.
Increasing the inlet operating pressure (if the process can withstand the pressure) is beyond the cavitation range.
Check load and work pressure. If the load is less than the design value, the pump may operate at a lower absolute pressure, which may lead to boiling of the sealed liquid and cavitation. Vacuum release valves or exhaust valves can be used to introduce additional loads so that the pump can operate closer to the design pressure.
A supercharger is installed upstream of the liquid ring vacuum pump. The supercharger will compress and increase the absolute suction pressure of the vacuum pump. There are many types of boosters, but the simplest type is a catapult without moving parts. The ejector uses the pressure energy of the power to increase the speed of the entrained gas load. This produces higher absolute pressure at the exit of the ejector. Two types of ejectors are steam ejectors using pressurized steam and air ejectors using atmospheric air as power.
If possible, increase the production of sealing fluid. This will reduce the temperature rise of the liquid ring pump and reduce the vapor pressure of the sealing fluid.
liquid ring vacuum pump operation
Once the liquid ring pump is started and operated, visual inspection should be carried out. Vacuum, temperature and pressure of sealing fluid should be checked and compared with design conditions. Bearing box should keep touch warm. Hot bearing boxes may indicate poor or worn or misaligned bearings.
The liquid ring vacuum pump is a very general machine. It can handle wet loads without metal-to-metal contact. It also acts like a direct contact condenser; it can absorb heat generated by compression, friction and condensation into the gas; it can absorb and remove any pollutants entrained in the gas. However, despite this versatility, the size and selection of the most economical system still requires complete information, not only about what fluid it will handle, but also how it will operate.
(The article comes from the Internet. If reprinting is not allowed, please contact our company to delete it.)
