vacuum valves classification
The valve is a mechanical device which controls the flow, direction, pressure and temperature of the fluid medium. It is a very important part of the pipeline system. This is the most complete valve classification, come and have a look!

The following is the valve classification organized by EVP vacuum pump manufacturer. There is no more complete valve classification than this one, right?
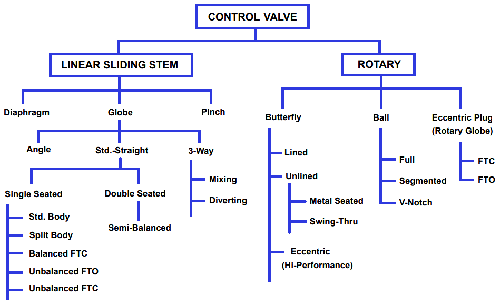
Valves have different requirements according to their types and uses, mainly including sealing, strength, regulation, circulation, opening and closing performance. In the design and selection of valves, in addition to the basic parameters and performance, the performance of the fluid should also be considered, including the phase state (gas, liquid or containing solid particles), corrosiveness, viscosity, toxicity, flammability and explosiveness, rarity and radioactivity of the fluid.
Classification by pressure:
Vacuum valve: PN lower than standard atmospheric pressure
Low pressure valve: PN ≤ 1.6Mpa
IP valve: PN = 2.5-6.4 MPa
High pressure valve: PN = 10-80 MPa
Ultra high pressure valve: PN ≥ 100 MPa
PS: PN refers to the nominal pressure, i.e. the maximum allowable working pressure of the valve at the reference temperature.

Classification by medium operating temperature:
High temperature valve: T > 450 ℃
Medium temperature valve: 120 ℃ < t ≤ 450 ℃
Normal temperature valve: – 30 ℃ ≤ t ≤ 120 ℃
Low temperature valve: t < – 30 ℃
Classification by nominal diameter:
Small diameter valve: DN < 40 mm
Medium diameter valve: DN = 40 – 300 mm
Large diameter valve: DN = 350 – 1200 mm
Oversize valve: DN ≥ 1400mm

Classification by drive mode:
Manual valve: with the help of handwheel, handle, lever or chain wheel, it is driven by manpower. When transmitting larger torque, it is equipped with gear and other deceleration devices.
Electric valve: driven by electric motor, electromagnetic or other electrical devices.
Hydraulic valve: driven by liquid (water, oil and other liquid media).
Pneumatic valve: driven by compressed air.

Classification by use:

1、 Gate valve
It refers to the valve that the closing piece (RAM) moves along the vertical direction of the channel center line. It is mainly used to cut off the pipeline, and also has the function of regulating the flow.
Gate valve features:
The fluid resistance is small.
The opening and closing moment is small.
The flow direction of the medium is not limited.
The length of the structure is short.
Good sealing performance.
The sealing surface is easy to be damaged.
The opening and closing time is long and the height is large.
There are many parts with complex structure, so it is difficult to manufacture and maintain.
Classification by valve plate structure
Rising stem gate valve: the stem thread and nut are not in contact with the medium and are not affected by the corrosiveness of the medium temperature. The opening degree is obvious and easy to see, so it is widely used.
Concealed stem gate valve: the screw thread and nut contact with the medium, which is affected by the medium temperature and corrosiveness, but the height and size of the valve are small. The concealed stem gate valve is suitable for non corrosive medium and the occasion with poor external environment condition.
According to whether the inner passage diameter of the valve body is the same
Reducing gate valve: the diameter at the valve seat is smaller than that at the flange connection.
Equal diameter gate valve: the diameter at the valve seat is consistent with that at the flange connection.
The diameter shrinkage can reduce the size of valve parts, reduce the force required for opening and closing, and expand the general scope of parts. However, the loss of fluid resistance will increase when the diameter is shrunk.

A ball with a middle opening is used as the valve center to control the opening and closing of the valve by rotating the ball. Ball valve can be straight, three-way or four-way. The ball valve is mainly used to cut off, distribute and change the direction of medium flow on the pipeline.
Because the ball valve seat is made of rubber material, its service temperature is limited. In order to deal with the possible fire situation, many designers use auxiliary metal to metal sealing. Ball valves are not suitable for throttling, but they can be used to reduce the pressure into or out of the system when they are partially open. In production equipment, ball valves are often used as open / close valves for general purposes.
Floating ball valve: the ball is floating. Under the action of medium pressure, the ball can produce a certain displacement and press on the sealing ring at the outlet to ensure the sealing at the outlet. The ball valve has simple structure and good sealing performance, but it has high pressure bearing and large operating torque at the outlet seal. This structure is widely used in medium and low pressure ball valves.
Fixed ball valve: the ball of this ball valve is fixed and does not move after being pressed. Generally, the upper and lower shafts integrated with the ball are equipped with rolling or sliding bearings, with small operating torque, suitable for high-pressure and large-diameter valves.
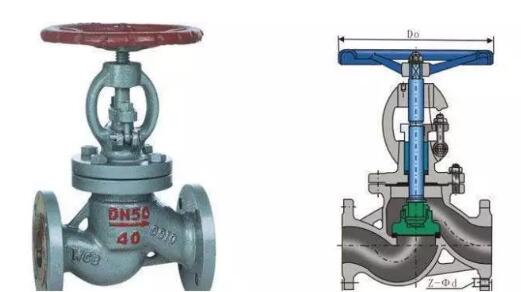
3、 Stop valve
The stem thread of the upper thread stem stop valve is outside of the medium, the stem thread is not subject to medium erosion, and it is also convenient for lubrication. This structure is widely used.
The stem thread of the lower thread stem stop valve is in direct contact with the medium in the valve body, which is not only unable to be lubricated, but also eroded by the medium. This structure is used for small caliber valves and medium with low temperature.
It refers to the valve with the closing piece (disc) moving along the center line of the valve seat, which is mainly used for cutting off on the pipeline.

4、 Check valve
Depending on the flow of the medium itself, the valve disc is automatically opened and closed. The medium can only flow in one direction, and the valve which can prevent the medium from flowing back is called check valve.
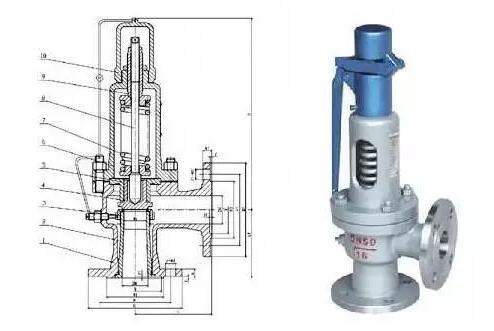
5、 Safety valve
Classification by load structure
Lever heavy hammer type safety valve: the heavy hammer is loaded on the valve disc through the lever, and the load hardly changes with the opening height. Due to the large size of the lever part of the safety valve, the whole valve is bulky, and the reseating pressure is low, which has been less used in the project.
Pilot type safety valve: composed of main valve and auxiliary valve. Medium pressure and spring pressure are loaded on the main valve disc at the same time. When overpressure occurs, the auxiliary valve disc is opened first, causing the main valve to open. It is mainly used in large diameter and high pressure applications.
Spring type safety valve: the spring force is loaded on the valve disc, and the load changes with the opening height. The advantages of the safety valve are small, light, high sensitivity, and the installation position is not strictly limited. It is widely used in oil and gas transportation projects.
Classification by opening height of safety valve
Micro lift safety valve: the opening height is 1 / 40-1 / 20 of the valve seat throat diameter, and it is usually made to gradually open (the opening height changes with the pressure). It is mainly used in liquid medium with small discharge capacity.
Full open safety valve: the opening height is equal to or greater than 1 / 4 of the valve throat diameter, which is usually made into a quick opening (the valve disc suddenly jumps up at a certain moment of opening to reach the full opening height). It is mainly used in gas and steam medium occasions and fluid medium occasions with large discharge capacity.
Gradual opening or quick opening safety valve: the opening height is between micro opening type and full opening type.
Classification by valve body construction
Totally enclosed: when discharging, the medium will not leak outwards and will be discharged completely through the discharge pipe.
Semi closed type: when discharging, one part of the medium is discharged through the discharge pipe, and the other part leaks out from the fitting of the valve cover and the valve stem.
Open type: when discharging, the medium is discharged directly from the top of the valve disc without passing through the discharge pipe.
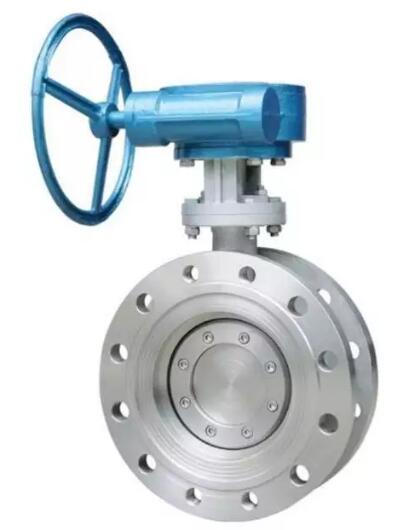

The disc is a disc, which rotates through the valve stem, and the disc rotates 90 degrees within the range of the valve seat to realize the opening and closing of the valve. It acts as a shut-off in the pipeline. The flow can also be adjusted.
characteristic
The opening and closing is convenient, quick, labor-saving, low fluid resistance, and can be operated frequently.
Simple structure, small volume and light weight.
It can transport mud and store the least liquid at the pipe mouth.
Under low pressure, good sealing can be achieved.
Good regulation performance.
The range of working pressure and temperature is small.
Poor sealing.
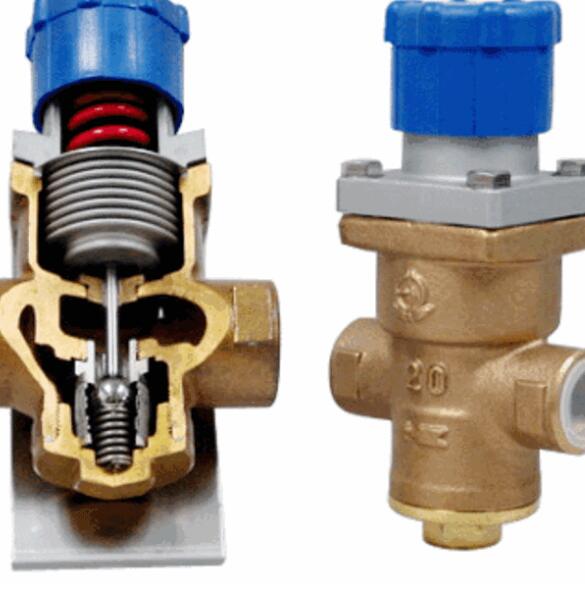

7、 Pressure reducing valve
The pressure reducing valve is an automatic valve to reduce the medium pressure to a certain value. Generally, the pressure behind the valve is less than 50% of the pressure in front of the valve. There are many kinds of pressure reducing valves, mainly piston type and spring film type.
The piston type pressure reducing valve is a valve to reduce pressure through the action of the piston. Spring film type pressure relief valve, is to rely on the spring and film to carry out pressure balance.

8、 Drain valve
The steam trap is also called the steam trap drain valve, steam water valve, steam trap, return water box, return water valve, etc. Its function is to automatically discharge the continuous condensate without letting the steam out.
The steam trap should be able to “identify” the steam and condensate, so as to play a role of steam blocking and drainage. The “identification” of steam and condensate is based on three principles: density difference, temperature difference and phase change. According to the three principles, three types of traps are made: mechanical type, thermal static type and thermal dynamic type.
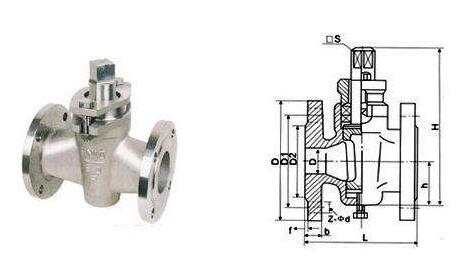
9、 Plug valve
The plug valve relies on the rotation of the plug body around the center line of the valve body to open and close. Its function is to cut off, divide the field and change the flow direction of medium. The utility model has the advantages of simple structure, small overall dimension, only 90 degree rotation during operation, and little fluid resistance. The disadvantage of the utility model is that the switch is laborious, the sealing surface is easy to wear, and it is easy to get stuck at high temperature, which is not suitable for regulating the flow.
Plug valve, also known as cock, cork, revolving door. It has many kinds, including straight through, three-way and four-way.

10、 Regulating valve
The regulating valve is used to regulate the flow, pressure and liquid level of the medium. According to the signal of the regulating part, the opening of the valve is automatically controlled, so as to achieve the regulation of medium flow, pressure and liquid level. The control valve is divided into electric control valve, pneumatic control valve and hydraulic control valve.
The regulating valve is composed of electric actuator or pneumatic actuator and regulating valve. The regulating valve is usually divided into two types: straight through single seat regulating valve and straight through double seat regulating valve. The latter has the characteristics of large flow capacity, small imbalance and stable operation, so it is usually especially suitable for occasions with large flow, high pressure drop and less leakage.
The regulating valve can be divided into straight stroke and angle stroke according to the stroke characteristics. Straight stroke includes: single seat valve, double seat valve, sleeve valve, cage valve, angle valve, three-way valve and diaphragm valve; angle stroke includes: butterfly valve, ball valve, eccentric rotary valve and full-function ultra light regulating valve.
The control valve can be divided into manual control valve, pneumatic control valve, electric control valve and hydraulic control valve according to the driving mode, that is, the pneumatic control valve with compressed air as the power source, the electric control valve with electricity as the power source, and the hydraulic control valve with liquid medium (such as oil) pressure as the power source;
According to the regulation form, it can be divided into regulation type, cut-off type and regulation cut-off type;
According to the flow characteristics, it can be divided into linear, logarithmic (percentage), parabola and fast opening.
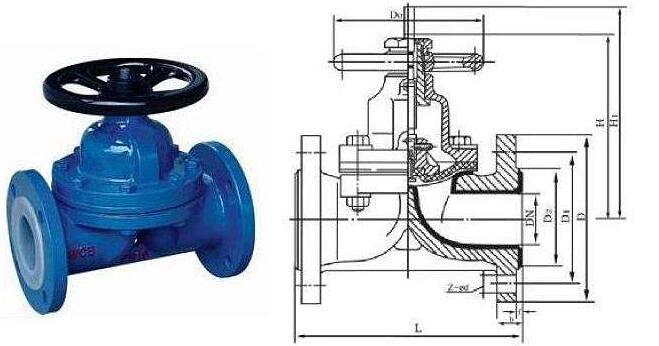
The valve body with corrosion-resistant lining and the corrosion-resistant diaphragm are used instead of the valve core components of the diaphragm valve, and the movement of the diaphragm is used for regulating. The valve body of diaphragm valve is made of cast iron, cast steel or cast stainless steel, and lined with various corrosion-resistant or wear-resistant materials, diaphragm material rubber and polytetrafluoroethylene. The lining diaphragm has strong corrosion resistance, which is suitable for the adjustment of strong corrosive medium such as strong acid and strong alkali.
The diaphragm valve has the advantages of simple structure, small fluid resistance, larger flow capacity than other valves of the same specification, no leakage, and can be used for the regulation of high viscosity and suspended particle medium. The diaphragm isolates the medium from the upper chamber of the valve stem, so there is no packing medium and no leakage. However, due to the limitation of diaphragm and lining materials, the pressure resistance and temperature resistance are poor, which are generally only applicable to 1.6Mpa nominal pressure and below 150 ℃.
The flow characteristic of the diaphragm valve is close to the quick opening characteristic, which is nearly linear before 60% stroke and little change after 60%. Pneumatic diaphragm valve can also be equipped with feedback signal, limiter, positioner and other devices to meet the needs of automatic control, program control or flow regulation. The feedback signal of pneumatic diaphragm valve adopts contactless sensing technology. The product adopts membrane type propulsion cylinder instead of piston cylinder, which eliminates the defect that the piston ring is easy to be damaged and causes leakage, which leads to the failure of valve opening and closing. When the air source fails, the hand wheel can be operated to open and close the valve.
The commonly used diaphragm valves are rubber lined diaphragm valve, fluorine lined diaphragm valve, unlined diaphragm valve and plastic diaphragm valve.
(The article comes from the Internet. If reprinting is not allowed, please contact our company to delete it.)
